Abstract
A persistent challenge in practical classification tasks is that labeled training sets are not always available. In particle physics, this challenge is surmounted by the use of simulations. These simulations accurately reproduce most features of data, but cannot be trusted to capture all of the complex correlations exploitable by modern machine learning methods. Recent work in weakly supervised learning has shown that simple, low-dimensional classifiers can be trained using only the impure mixtures present in data. Here, we demonstrate that complex, high-dimensional classifiers can also be trained on impure mixtures using weak supervision techniques, with performance comparable to what could be achieved with pure samples. Using weak supervision will therefore allow us to avoid relying exclusively on simulations for high-dimensional classification. This work opens the door to a new regime whereby complex models are trained directly on data, providing direct access to probe the underlying physics.
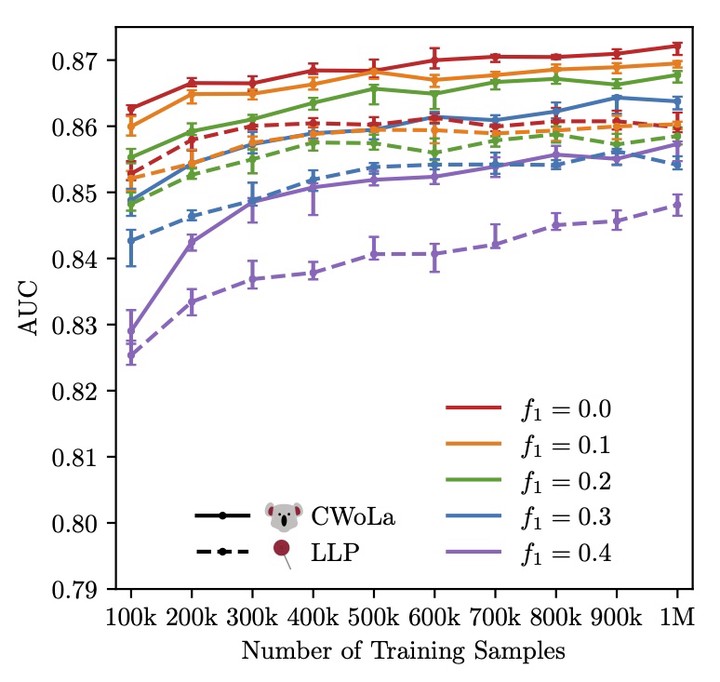
Figure 2: Performance of a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) operating on jet images trained with the CWoLa and LLP techniques for mixed samples with different purities and different numbers of training samples. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) goes up with more training samples, as expected, and is seen to be consistently higher for CWoLa than LLP. Both methods are able to achieve good classification performance on mixed samples with a wide variety of quark fractions, even down to samples with 40%/60% quarks.